LED lighting industry has been evolving for tens of years and there are always questions about “isolated and non-isolated” , which one is better? In the past, this kind of debate only existed in the low and mid power designs but nowadays, the question goes on to high power applications like sports lighting and harbor lighting.
My answer is that we can only say that which one is more suitable for certain applications or luminaire designs. Both of them have the reasons to be utilized in the market. And this article provides some ideas for luminaire designers on how to choose between the two kinds of LED drivers.

The difference between non-isolated and isolated LED driver
This figure below shows the details about the two structures. The key difference is about the isolation transformer which insulate the output from the high AC input voltage.
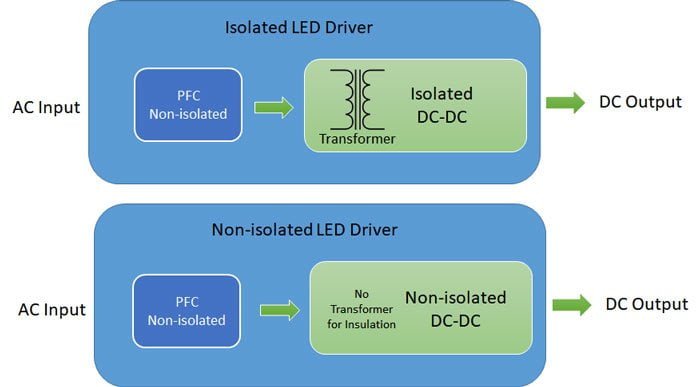
And the table below shows more about the electrical differences.
| Non-isolated | Isolated | |
|---|---|---|
| Topology | Buck,boost,buck-boost etc. | Flyback,forwardhalf bridge LLC etc. |
| Complexity | Low | Mid and high |
| Efficiency | High | Mid |
| Output Voltage | High | Mid and low |
| Output Safety | Unsafe | Relatively safe, safe SELV or class 2 can be achieved |
| Cost | 25%lower | 25% higher |
| Application | Built-in | Independent |
| Luminaire Design | More insulation needed | Easy |
Isolated dimming and isolated LED drivers
Both concepts can be easily mixed together when we are talking about “Isolated” since this word can be used for describing both dimming or LED driver itself. They are totally different concepts. Isolated dimming means that the dimming interface like DALI, 0-10V or PWM signals are insulated from input, output or physical earth. So no matter the LED driver output is safe or not, at least the dimming controllers which are connected directly to the luminaires are safe. And that is the reason isolated dimming should be employed by users. According to IEC61347-1, all the luminaires no matter non-isolated LED drivers are used or not, the dimming interface or circuitry has to be isolated separately. The electric strength level of input, output, case and dimming interface is shown as below table.
| Unit: Vac | Input | Output | Dimming | Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | – | – | 3750 | 1554 |
| Output | – | – | 1554 | 1554 |
| Dimming | 3750 | 1554 | – | 1554 |
| Case | 1554 | 1554 | 1554 | – |
How to choose and design with non-isolated LED drivers.
It is not easy to find a right non-isolated LED driver for high power design, the following has to be considered carefully:
a.Efficiency and thermal. Non-isolated LED drivers have the advantage efficiency compared with conventional isolated LED drivers. But it does not mean efficiency is not important. Better efficiency means lower power loss and less heat generation thus the LED LED driver can have longer life and higher reliability with better thermal situation. Checking the case temperature at Tc point is mandatory for a good luminaire design.
b.Dimming performance. Using a lower cost LED driver does not mean we have to sacrifice performance. Smooth dimming with either 0-10V or DALI or DMX control compatibility is important for stadium lights, especially the fast dimming response.
c.Find the right input voltage range for different countries.
d.Try to use the high LED voltage to achieve the best efficiency.
e.Utilize the LED board with higher insulation. 3kV insulation voltage is suggested.
f.Do adequate insulation for the whole luminaire to make sure that all the points that can be touched by human body are safe and able to pass insulation test.
uPowerTek’s high power non-isolated LED drivers are certified with UL, ENEC, CB and RCM, and they can be good choices for the high power applications.





